Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Seko, Noriaki; Bang, L. T.*; Tamada, Masao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 265(1), p.146 - 149, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:96.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)Radiation-induced graft polymerization is attractive technique for preparing metal-ion adsorbents. The reactive monomer of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) has been widely used for the syntheses of metal-ion adsorbents. This is because the GMA contains an epoxy group which can react easily with amine derivatives. Therefore, GMA-grafted polymer can be converted to various kinds of metal-ions adsorbents. Generally, GMA can be grafted by using organic solvent such as methanol and dimethyl sulfoxide. We found that the emulsion of GMA was available for effective grafting. The GMA was grafted onto polyethylene fiber (PE fiber) in the emulsion system. Polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20) was used as a surfactant to prepare the micelles of GMA in water. The degree of grafting reached 300% after the 1h grafting on 30 kGy irradiated PE fiber in the GMA emulsion obtained by mixture of 5% GMA, 0.5% Tween 20, and 94.5% water. Then, the GMA grafted PE fiber was chemically modified by using diethylene-triamine and triethylenetetramine and the amine-type adsorbents were obtained.
Kavakli, P. A.*; Kavakli, C.*; Seko, Noriaki; Tamada, Masao; G ven, O.*
ven, O.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 265(1), p.204 - 207, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:86.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)A novel nonwoven fabric was prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization of dimethylaminoethylmethacrylate (DMAEMA) onto polypropylene coated polyethylene nonwoven fabric. The trunk polymer was irradiated by electron beam at a voltage of 2 MeV and a current of 3 mA in a nitrogen atmosphere at dry-ice temperature at different doses. The degree of grafting was determined as a function of the total dose, monomer concentration, temperature, and reaction time. It was found that the degree of grafting of grafted polymer was greatly affected by reaction conditions. Grafting conditions were optimized, and about 150 % degree of grafting samples was used for further experiments. DMAEMA grafted polymer was later protonated by using acid solution to prepare adsorbent for the removal of anions. Adsorption experiments were performed in column mode for removal of hosphate. Approximately 2000 bed volumes of phosphate-free water can be produced from 10 ppb phosphate solution at high space velocity.
Xu, L.*; Yue, Z.*; Wang, M.*; Zhai, M.*; Yoshii, Fumio; Seko, Noriaki; Peng, J.*; Wei, G.*; Li, J.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 265(1), p.394 - 398, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.91(Instruments & Instrumentation)A water insoluble cellulose derivative, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate (HPMCP) hydrogels, was converted to Na type to form hydrogel in paste-like status by radiation crosslinking. Mechanism for radiation crosslinking of cellulose-derivatives in paste-like status was discussed. Crosslinkers, i.e., methyl 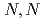 -bis-acrylamide (MBA) or ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) has been used to decrease gelation dose (Dg) of synthesis HPMCP hydrogels and improve its mechanical properties. MBA was found to be more effective for accelerating the crosslinking of HPMCP than EGDMA. Swelling degree of HPMCP hydrogel in many kinds ofsalt solutions followed Hofmeister series, which is ubiquitous in polyelectrolyte hydrogel. Specific reswelling was observed in concentrated KF solution, implying a very strong F
-bis-acrylamide (MBA) or ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) has been used to decrease gelation dose (Dg) of synthesis HPMCP hydrogels and improve its mechanical properties. MBA was found to be more effective for accelerating the crosslinking of HPMCP than EGDMA. Swelling degree of HPMCP hydrogel in many kinds ofsalt solutions followed Hofmeister series, which is ubiquitous in polyelectrolyte hydrogel. Specific reswelling was observed in concentrated KF solution, implying a very strong F binding ability of benzyl group. The comprehensive results obtained in this study will be utilized on the design of HPMCP-based controlled release system.
binding ability of benzyl group. The comprehensive results obtained in this study will be utilized on the design of HPMCP-based controlled release system.
Kavakli, C.*; Kavakli, P. A.*; Seko, Noriaki; Tamada, Masao; G ven, O.*
ven, O.*
no journal, ,
Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was grafted onto polypropylene coated polyethylene nonwoven fabrics in emulsion system by using radiation induced graft polymerization. For the preparation of GMA grafted fabric, the trunk PE/PP nonwoven fabric was irradiated by electron beam. After irradiation process, GMA was grafted onto irradiated nonwoven fabric under nitrogen atmosphere. In order to prepare fibrous PLE adsorbent for the removal of arsenic, grafted GMA was first modified with dipicolylamine. Maximum modification was obtained in 15 % (w/w) dipicolylamine solution. Then, PLE adsorbent was loaded with Cu ions. High copper ion loading was observed for PLE fibers. Column mode adsorption studies were conducted with copper loaded PLE adsorbents at different arsenic concentrations (1-50 ppm) and pH to examine the removal of arsenic (V) in aqueous solutions. The breakthrough point of As (V) was found to be 8000 bed volumes for 1 ppm As (V) solution.
ions. High copper ion loading was observed for PLE fibers. Column mode adsorption studies were conducted with copper loaded PLE adsorbents at different arsenic concentrations (1-50 ppm) and pH to examine the removal of arsenic (V) in aqueous solutions. The breakthrough point of As (V) was found to be 8000 bed volumes for 1 ppm As (V) solution.